Over the last 15 years, SEO shaped how businesses produced content, structured websites, and competed for consumer attention. But the landscape is shifting fast. Traditional search engines are no longer the sole entry point into the digital world. Generative engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Perplexity, and others, are becoming consumers’ first point of contact for information, decision-making, product recommendations, and brand discovery.
This shift has triggered a fundamental change: LLMs don’t prioritize the same signals that search engines do. The technical architecture of a website now matters as much as (and often more than) traditional blog content. For companies, this is not just a trend, it’s a strategic earthquake.
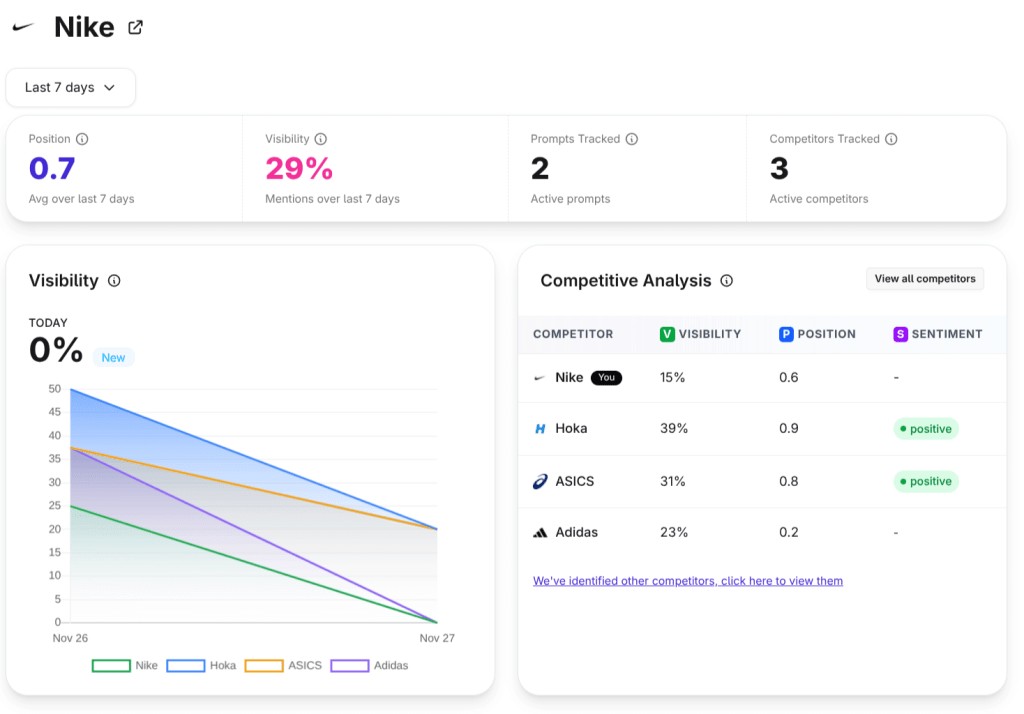
This article walks you through what changed, why it matters, and how organizations can adapt. If your brand needs to track its presence across multiple LLMs, this is exactly the landscape you need to understand.
Why LLMs don’t “Read the Web” the same way Google does
Traditional search engines work through crawling, indexing, ranking, and serving results from a database of URLs. Their core signals include backlinks, keyword relevance, content freshness, metadata, and domain authority. LLMs do something entirely different.
LLMs learn from snapshots, structured data, and curated pipelines
While each model has proprietary methods, the pattern is consistent:
- They consume highly structured sources (Wikipedia, Common Crawl, academic corpora, open datasets).
- They rely on technical files such as
robots.txt,sitemap.xml, and emerging conventions likellms.txt. - They ingest large portions of the web in compressed form, not page-by-page like Google.
- They don’t “rank” content, they synthesize it.
- They use retrieval-augmented learning when connected to the live web, meaning structured data matters more than long-form copy.
In practice, this means: Your blog posts still matter, but your site’s technical clarity matters more.
Here are the most critical technical aspects you need to ensure your website adheres to, to ensure LLMs can process it:
1. llms.txt
Emerging standards like llms.txt are designed to tell generative engines:
- what parts of the site may be used for training
- what metadata is available
- which files contain authoritative information
- how product and service descriptions should be interpreted
It’s early, but adoption is accelerating.
2. sitemap.xml
Search crawlers use sitemaps, but LLM pipelines rely on them even more, as they provide:
- canonical URLs
- relationships between pages
- data freshness indicators
- priority of content
- structured definitions of product categories and brand entities
A clean, accurate sitemap shapes how your brand is understood in model training pipelines.
3. robots.txt
This is an additional file you need to host alongside your sitemap, which determins:
- what can be ingested by AI models
- how scrapers interact with your site
- which datasets include your content in future training cycles
Some companies unknowingly block their entire presence from LLMs.
4. Structured Data (schema.org)
Models interpret structured markup (products, reviews, pricing, company info, FAQs) as high-confidence facts.
A page with rich JSON-LD often influences an LLM more than a 2,000-word article.
5. Repetition Across Trusted Sources
Unlike Google, LLMs don’t operate on a single live index. Instead, they depend on seeing the same information repeated across several independent sources. If your brand appears:
- in your own site
- in partner sites
- in product directories
- in trusted public datasets
- in reviews
- in standardized schemas
…it becomes far more likely the model will surface your company in its answers.
The Bottom Line
We’re living through the biggest shift in digital discovery since the rise of search engines. LLMs are becoming the new default interface for information, and if businesses don’t adapt, they’ll simply vanish from AI-generated answers.
The companies that understand and invest in LLM visibility tracking now will dominate the next decade of digital presence.
You must be logged in to post a comment.